前文介绍了代理模式及实现,但想要实现一个完整的AOP框架还远远不够,接下来我们来分析一下Spring是如何实现AOP的。
1 AOP体系结构
下图AOP联盟定义的AOP体系结构,大致分为从使用到实现的三个层次。整篇文章都将按照这三个层次进行分析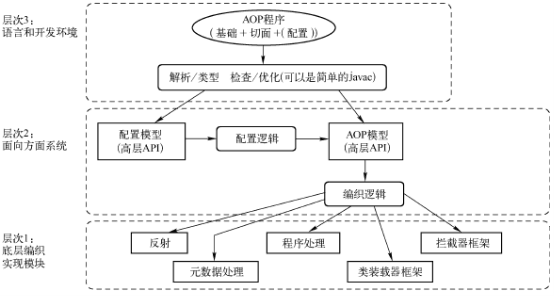
1.1 层次3:语言和开发环境
- 基础:可以视为待增强对象
- 切面:通常包含对于基础的增强应用
- 配置:指配置环境或编织配置,将基础和切面结合起来,从而实现对目标对象的编织实现
Spring使用Java语言来实现增强对象和切面,并为这两者提供配置环境;对于编织配置,可以使用IoC容器来完成,而Ioc恰恰是Spring的强项。
1.2 层次2:面向方面系统
面向方面系统为上层的语言与开发环境提供支持,将基础、切面和配置封装成面向方面中的逻辑模型。
1.3 层次1:底层编织实现模块
将编织逻辑进行实现的技术。
前文所述的两种动态代理技术就是在这个层面进行应用。
2 Spring AOP实现
我们从上到下的看看Spring如何实现AOP的。整个AOP框架逻辑流程很复杂,这里就只对在目标对象在单例模式下并使用JDK动态代理的AOP进行分析。
2.1 层次3:语言和开发环境
2.1.1 基础
在Spring中,基础就是你配置的Bean对象,这个Bean对象可以配置在XML中,也可以使用注解进行配置,如<bean id="realSubject" class="com.magicalwolf.proxy.RealSubject" />
2.1.2 切面
在Spring中,切面由切点和通知组成,由使用者进行定义.
PointCut切点
决定Advice通知应该作用于哪个连接点,也就是通过切点定义哪些方法需要增强。
PointCut接口是所有切点实现的基本接口,其中定义了MethodMatcher方法,用来判断当前方法是否需要增强。可以通过不同的方式进行判断,如JdkRegexpMethodPointcut类使用正则表达式进行匹配,还可以使用类限定名,切点表达式等方式进行匹配。
Advice通知
通知定义在连接点做什么,为切面增强提供织入接口。Advice接口是AOP联盟定义的统一接口,Spring对这个接口进行了细化和扩展,如BeforeAdvice,AfterAdvice,ThrowsAdvice
Advisor通知器
通知器将通知和切点结合起来,为Spring配置AOP容器提供便利。
2.1.3 配置
对基础和切面进行配置,使之对基础进行增强.Spring实现多种方式的配置,ProxyFactoryBean完成声明式配置,ProxyFactory完成编程式配置。AspectJProxyFactory将Spring和Aspectj集成。
2.1.4 使用ProxyFactoryBean的示例
applicationContext.xml
RequestBeforeAdvice.java
Main.java
层次3主要定义了开发人员如何使用AOP,Spring在背后将进行逻辑模型的封装工作
2.2 层次2:面向方面系统
我们从ProxyFactoryBean出发,看看面向方面系统是如何对target目标起作用的。
2.2.1 ProxyFactoryBean的继承关系
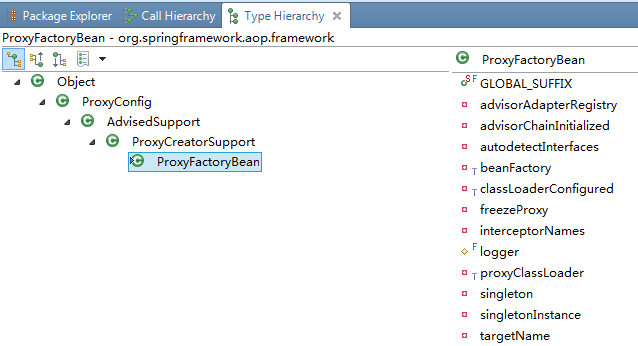
ProxyFactoryBean类负责具体AOP代理对象的生成ProxyCreateSupport类是创建AOP代理对象的一个辅助类AdvisedSupport类封装了对通知和通知器相关的操作ProxyConfig类为子类提供配置属性
2.2.2 生成代理对象跟踪
从FactoryBean中获取对象,是以getObject()方法为入口,在ProxyFactoryBean也是如此,getObject()方法对目标对象进行增强处理。
2.2.2.1 public Object getObject()
首先对通知器链进行初始化,生成代理对象时如果是单例模式调用getSingletonInstance(),此处只分析单例的情况
2.2.2.2 private synchronized void initializeAdvisorChain()
初始化通知器链,此方法是线程安全的
2.2.2.3 private synchronized Object getSingletonInstance()
|
|
2.2.2.4 protected Object getProxy(AopProxy aopProxy)
AopProxy是一个接口,有两个子类实现,一个是ObjenesisCglibAopProxy,一个是JdkDynamicProxy.分别通过CGLIB和JDK来生成需要的Proxy代理对象
2.2.2.5 protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy()
此方法在ProxyCreatorSupport中定义,具体是通过AopProxyFactory来获得AopProxy,AopProxyFactory默认的工厂实现是DefaultAopProxyFactory,生成哪一种AopProxy就在此类中定义
DefaultAopProxyFactory中的createAopProxy方法
JdkDynamicAopProxy中的getObject方法,这里我们可以看到熟悉的Proxy.newProxyInstance()方法
2.2.2.6 private void addAdvisorOnChainCreation(Object next, String name)
namedBeanToAdvisor方法会将next对象包装为Advisor对象,并添加到Advisor集合中
在namedBeanToAdvisor方法中,会使用DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry的warp方法对next对象进行包装.通知器是由切点和通知组成,如果只配置了通知,则切点为默认的TruePointcut,它对任何方法的匹配都将返回true
通过以上的分析,我们已经得到了代理对象,至此层次2的工作已经完成了,层次3获得的配置模型,在配置逻辑的应用下向AOP模型转换,接下来该层次1的实现了
2.2 层次1:底层编织实现模块
在生成代理对象的时候,相关的拦截器已经配置完成,拦截器起作用是通过对方法进行回掉完成的。
2.2.1 使用JDK代理的实现
前文提到过,在JDK代理中方法回掉的入口是在invoke方法中。而JdkDynamicAopProxy实现了InvocationHandler接口,方法回掉逻辑也定义在其中.
invoke方法获取目标对象和拦截器链,并生成ReflectiveMethodInvocation对象,通过这个对象完成对AOP功能的封装。
2.2.2 获得方法的拦截器链
|
|
methodCache是一个集合MapDefaultAdvisorChainFactory来生成拦截器链
此方法有一个适配和注册的过程,它将Advice通知适配成Spring预先设计好的拦截器。适配和注册的工作是在GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry的getInterceptors()中完成的
来看一下MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter
将Advice封装成了MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor,此类中有invoke方法,会先调用advice的before方法
至此,Spring AOP实现了对advice的织入,可以看到它将xml中配置的通知器适配成了拦截器
2.2.3 方法调用
之前讲到了拦截器的适配和注册,对呀没有拦截器的方法直接调用,有拦截器的方法会构造ReflectiveMethodInvocation,并沿着拦截器链进行调用。整个调用链的入口在proceed方法中
至此,完成对拦截器链及目标方法的调用
3 总结
3.1 层次3:语言与开发环境
Spring AOP使用Java语言,可以通过多种方式进行AOP配置,基础就是Bean对象,切面可以通过xml或注解进行声明.配置是由IoC容器完成的
3.2 层次2:面向方面系统
本文分析使用ProxyFactoryBean的情况,ProxyFactoryBean处理配置逻辑,生成代理对象。ProxyFactoryBean会先初始化通知器集合,再根据代理类型使用JdkDynamicProxy或ObjenesisCglibAopProxy生成代理对象
3.1 层次1:底层编织实现模块
使用JDK代理时,方法的回掉入口在invoke方法中,在invoke方法中实现了Advice的织入,以及目标方法的调用。
- Advice的织入:Spring预先设计好了拦截器,如
MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor,AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor,ThrowsAdviceInterceptor,将Advice适配成对应的拦截器,并将拦截器链缓存,此时完成了对Advice的织入 - 目标方法的调用:如果在目标方法未配置拦截器,则直接调用目标方法,如果得到了拦截器链,则沿着拦截器链执行。在执行过程中如果是动态匹配的拦截器,则需要再次进行匹配,否则直接调用拦截器。
以上分析了Spring AOP的部分实现,不过整个AOP基本流程已经分析完成。有了基础再去看AOP的高级部分会更加容易